Robotic Surgery: Revolutionizing Healthcare
Advancements in technology have revolutionized various industries, and healthcare is no exception. One groundbreaking innovation that has gained significant attention in recent years is robotic surgery. This cutting-edge approach combines the expertise of skilled surgeons with the precision and dexterity of robotic systems, promising improved outcomes and enhanced patient care.
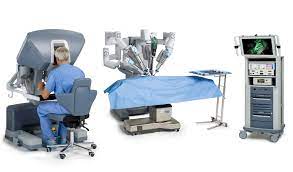
Robotic surgery involves the use of robotic arms controlled by highly trained surgeons. These robotic arms are equipped with tiny instruments and a high-definition camera, allowing for precise movements and providing a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical site. The surgeon operates the system from a console, controlling every movement with exceptional precision.
One of the key advantages of robotic surgery is its ability to perform minimally invasive procedures. Traditional open surgeries often require large incisions, leading to longer recovery times, increased pain, and higher risks of complications. Robotic surgery, on the other hand, utilizes small incisions, resulting in reduced trauma to surrounding tissues and faster healing.
The enhanced precision offered by robotic systems also contributes to improved surgical outcomes. The robotic arms can rotate 360 degrees and bend in ways that human hands cannot, allowing surgeons to access hard-to-reach areas with greater ease. This increased range of motion enables intricate procedures that were previously challenging or impossible to perform using conventional methods.
Moreover, robotic surgery offers numerous benefits for both patients and surgeons. Patients often experience less blood loss during procedures performed using robotics compared to traditional methods. Additionally, smaller incisions mean reduced scarring and decreased risk of infection. Patients also tend to have shorter hospital stays and quicker recoveries, allowing them to return to their daily lives sooner.
For surgeons, the use of robotics can alleviate physical strain during lengthy procedures as they operate from a comfortable console rather than directly at the operating table. The system’s intuitive controls translate the surgeon’s hand movements into precise motions by the robotic arms. This level of control enhances surgical accuracy while minimizing the potential for human error.
Robotic surgery has proven successful in various medical specialties, including urology, gynecology, general surgery, and cardiothoracic surgery. Procedures such as prostatectomies, hysterectomies, gallbladder removals, and even heart surgeries are now being performed using robotic systems.
However, it is important to note that robotic surgery is not a replacement for skilled surgeons. Rather, it serves as a valuable tool that enhances their capabilities and improves patient outcomes. Surgeons undergo extensive training to master the robotic systems and ensure safe and effective use during procedures.
As with any medical advancement, there are considerations to be aware of. Robotic surgery can be costlier than traditional methods due to the initial investment in equipment and ongoing maintenance. Additionally, not all surgical procedures can benefit from robotics, and each case should be evaluated individually to determine the most appropriate approach.
In conclusion, robotic surgery represents a significant leap forward in healthcare technology. Its ability to combine the precision of robotics with the expertise of surgeons offers numerous advantages for patients and healthcare providers alike. With ongoing advancements and continued research in this field, we can expect robotic surgery to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of surgical care.
Frequently Asked Questions About Robotic Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is robotic surgery?
- What are the benefits of robotic surgery?
- How safe is robotic surgery?
- What conditions can be treated with robotic surgery?
- Are there any risks associated with robotic surgery?
- How long does a typical robotic surgery procedure take?
What is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery is a state-of-the-art surgical technique that combines the skills of highly trained surgeons with the precision and versatility of robotic systems. It involves the use of robotic arms equipped with specialized instruments and a high-definition camera to perform surgical procedures with enhanced precision and control.
During a robotic surgery procedure, the surgeon sits at a console in the operating room, controlling the robotic arms remotely. The surgeon’s hand movements are translated into precise motions by the robotic system, allowing for intricate maneuvers and delicate procedures. The surgeon views a magnified, three-dimensional image of the surgical site on a monitor, providing enhanced visibility and accuracy.
The robotic arms used in these procedures are designed to mimic human hand movements but with greater dexterity and range of motion. They can rotate 360 degrees and bend in ways that human hands cannot, enabling access to difficult-to-reach areas within the body.
Robotic surgery offers several advantages over traditional open surgery or even laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery. It allows for smaller incisions, resulting in reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, less blood loss, and faster recovery times for patients. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery often leads to shorter hospital stays, decreased post-operative pain, reduced scarring, and lower risks of complications such as infection.
The precise control provided by robotic systems also enhances surgical outcomes. Surgeons can perform complex procedures more accurately due to improved visualization and greater maneuverability of instruments. This can be particularly beneficial for intricate surgeries involving delicate tissues or structures.
It is important to note that while robotics play a crucial role in surgical procedures, they are not autonomous systems. Skilled surgeons who have undergone specialized training operate the robots throughout the procedure. The surgeon’s expertise combined with robotic assistance results in optimal patient care.
Robotic surgery has been successfully used across various medical specialties including urology, gynecology, general surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, and more. It continues to evolve and expand its applications as ongoing research and technological advancements enhance its capabilities.
Overall, robotic surgery represents a significant advancement in surgical techniques, offering improved precision, shorter recovery times, and better patient outcomes. It is an exciting development that has the potential to reshape the future of surgical care.
What are the benefits of robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery offers several benefits that contribute to improved patient outcomes and enhanced surgical care:
- Minimally Invasive: Robotic surgery utilizes small incisions, resulting in reduced trauma to surrounding tissues. This leads to less pain, minimal scarring, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgeries.
- Enhanced Precision: The robotic arms used in robotic surgery offer a greater range of motion and more precise movements than human hands. This allows surgeons to access hard-to-reach areas with greater ease and perform intricate procedures with enhanced accuracy.
- Magnified 3D Vision: Robotic systems provide surgeons with a high-definition, three-dimensional view of the surgical site. This detailed visualization enables better depth perception and helps surgeons navigate complex anatomical structures more effectively.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Robotic surgery techniques often result in reduced blood loss during procedures compared to traditional methods. This can lead to decreased transfusion requirements and lower risks associated with excessive bleeding.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Patients who undergo robotic surgery typically experience shorter hospital stays compared to those who undergo traditional open surgeries. The minimally invasive nature of robotic procedures allows for quicker recoveries, enabling patients to return to their normal activities sooner.
- Faster Recovery Time: With smaller incisions and reduced trauma to tissues, patients undergoing robotic surgery often experience faster recovery times. This means less time spent in post-operative care and a quicker return to daily life.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: The precision and accuracy offered by robotic systems can minimize the risk of complications during surgical procedures. Surgeons have better control over their movements, reducing the potential for human error.
- Improved Surgical Access: Robotic arms can rotate 360 degrees and bend in ways that human hands cannot replicate easily. This flexibility allows surgeons to access challenging anatomical locations more easily, expanding the range of procedures that can be performed using minimally invasive techniques.
- Surgeon Ergonomics: Robotic surgery systems provide surgeons with a comfortable console from which they can operate. This reduces physical strain during lengthy procedures and allows for more precise movements, enhancing surgical accuracy.
- Patient Satisfaction: The benefits of robotic surgery, such as smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery, and improved outcomes, contribute to higher patient satisfaction levels. Patients appreciate the advantages offered by this advanced technology.
It is important to note that the specific benefits of robotic surgery may vary depending on the procedure and individual patient circumstances. It is always advisable to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate surgical approach for each case.
How safe is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery has demonstrated a high level of safety, but like any surgical procedure, it is not without potential risks. It is important to understand that the safety of robotic surgery depends on various factors, including the skill and experience of the surgeon, proper patient selection, and adherence to established protocols.
One of the primary advantages of robotic surgery is its precision and accuracy. The robotic arms can perform delicate movements with great precision, minimizing the risk of human error. Additionally, the high-definition 3D visualization provided by robotic systems allows surgeons to have a detailed view of the surgical site, further enhancing safety.
Furthermore, robotic surgery often involves smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgeries. Smaller incisions generally result in less blood loss, reduced risk of infection, and faster recovery times for patients.
However, it is crucial to note that complications can still occur during robotic procedures. Some potential risks include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding tissues or organs, adverse reactions to anesthesia or medications used during surgery, and equipment malfunction. These risks are not exclusive to robotic surgery but are inherent in any surgical procedure.
To mitigate these risks and ensure patient safety during robotic surgeries, several measures are taken. Surgeons undergo specialized training in using robotic systems before performing procedures independently. Surgical teams follow established protocols and guidelines specific to robotic surgery techniques. Patient selection criteria are carefully evaluated to identify suitable candidates for this approach.
It is essential for patients considering robotic surgery to have open and detailed discussions with their surgeons regarding potential risks and benefits specific to their individual circumstances. Surgeons should provide clear explanations about the procedure itself as well as any associated risks or possible complications.
In summary, while robotic surgery has shown promising results in terms of safety and patient outcomes, it is crucial that procedures are performed by skilled surgeons who have undergone appropriate training. Adherence to established protocols and thorough patient evaluation contribute significantly to ensuring safe outcomes in robotic surgeries. As with any medical procedure, patients should have open communication with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
What conditions can be treated with robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery has expanded its applications across various medical specialties, allowing for the treatment of a wide range of conditions. Some of the conditions that can be treated with robotic surgery include:
- Prostate Cancer: Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy is a commonly performed procedure for the treatment of localized prostate cancer. The precision and dexterity of robotic systems aid in removing the prostate gland while preserving surrounding nerves and tissues, minimizing the risk of complications such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
- Gynecological Conditions: Robotic surgery is used for various gynecological procedures, including hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), myomectomy (removal of uterine fibroids), and endometriosis treatment. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery allows for faster recovery, reduced scarring, and improved outcomes compared to traditional open surgeries.
- Colorectal Conditions: Robotic-assisted colorectal surgeries are performed to treat conditions such as colon cancer, rectal cancer, diverticulitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. The precise movements and enhanced visualization provided by robotic systems enable surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy.
- Cardiothoracic Conditions: Robotic surgery has made significant advancements in cardiothoracic procedures like mitral valve repair/replacement, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and lung lobectomy. The high-definition visuals and precise movements facilitate intricate cardiac and pulmonary surgeries with reduced trauma to the patient.
- Urological Conditions: In addition to prostate cancer treatment mentioned earlier, robotic surgery is utilized in other urological procedures such as partial nephrectomy (kidney tumor removal), pyeloplasty (repairing blocked kidney drainage), cystectomy (bladder removal), and urinary tract reconstruction.
- General Surgery: Robotic-assisted techniques are employed in various general surgical procedures such as gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), hernia repair, and bariatric surgery (weight-loss surgery). The robotic system’s flexibility and maneuverability aid surgeons in performing these procedures with enhanced precision.
It is important to note that the suitability of robotic surgery for a specific condition may vary depending on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the procedure, and the surgeon’s expertise. Each case should be evaluated individually to determine the most appropriate treatment approach, whether it involves robotic surgery or other methods.
Are there any risks associated with robotic surgery?
While robotic surgery offers numerous benefits, like any medical procedure, it does come with certain risks. It is important for patients to be aware of these potential risks and have open discussions with their healthcare providers before making any decisions. Some of the risks associated with robotic surgery include:
- Technical failures: Like any technology, robotic systems can experience technical malfunctions or failures during a procedure. While these instances are rare, they can potentially impact the surgery and require the surgeon to switch to an alternative method.
- Surgeon learning curve: Robotic surgery requires specialized training for surgeons to become proficient in operating the system effectively. During the learning curve, there may be a slight increase in surgical time or a higher risk of complications until surgeons gain sufficient experience.
- Limited tactile feedback: Robotic systems lack the sense of touch that human hands possess. This absence of tactile feedback means that surgeons rely solely on visual and auditory cues during the procedure. Although advanced imaging technology compensates for this limitation, some subtle sensations may not be fully transmitted to the surgeon.
- Equipment-related complications: The use of robotic instruments introduces the possibility of equipment-related complications such as instrument failure, unintended movement, or accidental damage to surrounding tissues. Surgeons and their teams must remain vigilant throughout the procedure to minimize these risks.
- Surgical team coordination: Robotic surgery involves a multidisciplinary team working together seamlessly during procedures. Effective communication and coordination among team members are crucial to ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes.
- Potential for longer operating times: While robotic surgery aims to improve efficiency, it may sometimes result in longer operating times compared to traditional methods due to factors such as setup time, docking of robotic arms, or instrument changes during complex procedures.
- Cost considerations: Robotic surgery can be more expensive than traditional approaches due to initial investment costs, maintenance expenses, and specialized training requirements for surgeons and staff involved in its operation.
It is important to note that the risks associated with robotic surgery are generally low and often outweighed by the potential benefits. Surgeons undergo rigorous training to mitigate these risks and ensure patient safety. Each surgical case is unique, and the decision to proceed with robotic surgery should be made after careful consideration of individual circumstances, in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional.
Patients should openly discuss any concerns or questions they have regarding robotic surgery with their surgeon to gain a comprehensive understanding of the procedure and its potential risks.
How long does a typical robotic surgery procedure take?
The duration of a robotic surgery procedure can vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon’s experience, and the patient’s specific condition. Generally, robotic surgeries tend to take longer than traditional open surgeries due to the setup and calibration of the robotic system.
While it is challenging to provide an exact timeframe for a “typical” robotic surgery procedure, it can range from one to several hours. Some procedures may be relatively quick and completed within two hours, while others may take significantly longer, lasting four hours or more.
It’s important to note that the duration of surgery is not solely determined by the use of robotics but also by other factors such as patient characteristics and surgical requirements. Surgeons prioritize patient safety and ensure that sufficient time is allocated for each step of the procedure to achieve optimal outcomes.
During pre-surgical consultations, surgeons can provide patients with a more accurate estimate of how long their specific robotic surgery procedure is expected to take. They will consider individual factors and discuss any potential variations in surgical duration based on their expertise and experience with similar cases.
Ultimately, while robotic surgery procedures may require more time compared to traditional methods, this additional time investment often translates into improved precision, reduced complications, faster recovery times, and better overall outcomes for patients.