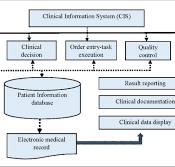
The Importance of Clinical Information Systems in Modern Healthcare
In today’s rapidly advancing healthcare landscape, the role of clinical information systems has become increasingly crucial. A clinical information system is a computer-based technology designed to manage and store healthcare data for healthcare providers, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient care.
One of the key benefits of clinical information systems is their ability to streamline processes and improve efficiency in healthcare settings. By digitising patient records, test results, prescriptions, and other essential data, clinicians can access information quickly and accurately, leading to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, clinical information systems promote collaboration among healthcare professionals by allowing seamless sharing of patient data across different departments and facilities. This interconnected approach enhances communication, reduces errors, and ultimately improves the quality of care delivered to patients.
Another significant advantage of clinical information systems is their role in supporting evidence-based practice. By analysing large datasets and trends in patient outcomes, healthcare providers can identify best practices and tailor treatments to individual patients based on proven effectiveness.
Moreover, clinical information systems play a vital role in enhancing patient safety. Features such as medication alerts, allergy warnings, and decision support tools help prevent medical errors and adverse events that could harm patients.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of clinical information systems. From electronic health records to telemedicine platforms, these systems are at the forefront of transforming healthcare delivery by promoting efficiency, collaboration, evidence-based care, and patient safety.
In conclusion, the adoption of clinical information systems is essential for modern healthcare organisations looking to improve patient outcomes, enhance quality of care, and adapt to the ever-changing demands of the industry. By leveraging technology effectively, healthcare providers can revolutionise the way they deliver services and ultimately benefit both patients and providers alike.
Understanding Clinical Information Systems: Key Questions and Answers
- Which definition best describes clinical information systems?
- What is the meaning of clinical information?
- What are examples of an his?
- What is an example of a clinical information system?
- What is the difference between AIS and CIS?
- Is CIS the same as EHR?
- What is a cis system?
Which definition best describes clinical information systems?
A clinical information system can be best described as a computer-based technology that is specifically designed to manage and store healthcare data for healthcare providers. This system enables clinicians to access and utilise essential patient information such as medical records, test results, treatment plans, and prescriptions efficiently. By centralising and digitising this data, clinical information systems facilitate informed decision-making, improve communication among healthcare professionals, enhance patient safety through alerts and reminders, and support evidence-based practice by analysing trends in patient outcomes. In essence, clinical information systems play a pivotal role in modern healthcare by optimising processes, promoting collaboration, and ultimately enhancing the quality of care delivered to patients.
What is the meaning of clinical information?
Clinical information refers to data and insights gathered during the course of patient care within a healthcare setting. It encompasses a wide range of information, including medical history, test results, treatment plans, medications prescribed, and any other relevant details related to a patient’s health and well-being. The primary purpose of clinical information is to support healthcare professionals in making informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care for patients. By capturing and organising this data in a structured manner, clinical information systems play a vital role in improving the quality, safety, and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
What are examples of an his?
An example of an HIS, or Hospital Information System, is a comprehensive software solution that integrates various functions within a healthcare facility. This system typically includes modules for patient registration, appointment scheduling, medical records management, billing and invoicing, inventory management, and more. By centralising these functions into a single platform, HIS streamlines operations, enhances communication between departments, and improves overall efficiency in delivering patient care.
What is an example of a clinical information system?
A prime example of a clinical information system is an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. EHRs are digital versions of patients’ paper charts, containing comprehensive information about their medical history, diagnoses, medications, treatment plans, immunization dates, allergies, radiology images, and laboratory test results. These systems streamline healthcare processes by providing a centralised platform for healthcare professionals to access and update patient data securely. EHRs enhance communication among care team members and support evidence-based decision-making to improve patient care outcomes.
What is the difference between AIS and CIS?
When comparing AIS (Administrative Information System) and CIS (Clinical Information System) in the context of healthcare, it’s important to understand their distinct roles. AIS primarily focuses on managing administrative tasks such as billing, scheduling, and financial operations within a healthcare organisation. On the other hand, CIS is specifically designed to handle clinical data related to patient care, including medical records, test results, treatment plans, and other critical information used by healthcare providers to make informed decisions. While AIS streamlines operational processes, CIS plays a vital role in improving patient care quality and safety by facilitating the efficient management and exchange of clinical data among healthcare professionals.
Is CIS the same as EHR?
In the realm of healthcare technology, a common question that often arises is whether Clinical Information Systems (CIS) are the same as Electronic Health Records (EHR). While there is some overlap between the two terms, they serve distinct purposes in the healthcare ecosystem. A CIS typically refers to a broader system that encompasses various applications for managing clinical data within a healthcare facility, including functions like order entry, results reporting, and decision support. On the other hand, an EHR specifically focuses on digitising and storing individual patient health records in a longitudinal format that can be accessed and shared across different healthcare providers. Understanding the nuances between CIS and EHR is essential for healthcare professionals seeking to optimise their use of technology in delivering quality patient care.
What is a cis system?
A Clinical Information System (CIS) is a sophisticated computer-based technology used in healthcare settings to manage and store crucial patient data, medical records, and other clinical information. Essentially, a CIS serves as a centralised platform that enables healthcare providers to access, update, and share vital patient information efficiently. By digitising and organising patient data, a CIS enhances the quality of care by facilitating accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of patient progress. It plays a pivotal role in streamlining healthcare processes, promoting collaboration among healthcare professionals, and ultimately improving patient outcomes.