CABG Surgery: A Lifesaving Procedure for Heart Health
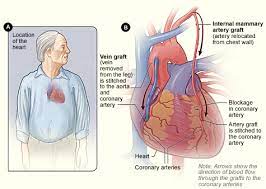
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery, also known as heart bypass surgery, is a medical procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of coronary heart disease. It is a highly effective and often lifesaving intervention for individuals suffering from blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart.
Coronary heart disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged with plaque, a buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits. This can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and even heart attacks.
CABG surgery involves creating new pathways for blood to flow around the blocked or narrowed arteries. During the procedure, a skilled cardiac surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, such as the leg or chest wall, and attaches it to bypass the damaged section of the artery. This creates an alternate route for oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart muscle, improving its supply and reducing symptoms.
The decision to undergo CABG surgery is typically made after careful consideration by both patient and medical professionals. Factors such as severity of symptoms, extent of blockages in the arteries, overall health condition, and response to other treatment options are taken into account.
The procedure itself is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. The surgeon makes an incision in the chest and uses special instruments to access the heart. The bypass grafts are carefully connected to reroute blood flow around blocked areas. Once completed, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples.
Recovery from CABG surgery varies from person to person but generally involves a hospital stay of about one week. During this time, patients are closely monitored by healthcare professionals who ensure proper healing and manage pain effectively. Post-surgery rehabilitation programs may be recommended to help restore strength and improve cardiovascular fitness.
CABG surgery has proven to be highly successful in improving the quality of life for many individuals with coronary heart disease. It can alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of future heart attacks, and increase life expectancy. However, it is important to note that CABG surgery is not a cure for heart disease. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking, are crucial in maintaining long-term heart health.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with CABG surgery. These can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, stroke, or damage to surrounding organs. However, advancements in surgical techniques and post-operative care have significantly reduced the occurrence of these complications.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of coronary heart disease or have been diagnosed with blocked arteries, it is essential to consult with a qualified cardiac specialist. They will assess your individual situation and determine whether CABG surgery is the most appropriate course of action.
CABG surgery has transformed the lives of countless individuals by restoring blood flow to the heart and improving overall cardiac function. With ongoing advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, this procedure continues to offer hope and improved outcomes for those affected by coronary heart disease.
Frequently Asked Questions About CABG Surgery in the UK
- What is CABG surgery?
- What are the risks of CABG surgery?
- How long does CABG surgery take?
- What is the recovery time for CABG surgery?
- How successful is CABG surgery?
- Are there any alternatives to CABG surgery?
- Is there any follow-up care after CABG surgery?
What is CABG surgery?
CABG surgery, also known as Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting, is a surgical procedure performed to treat coronary heart disease. It involves creating new pathways for blood to flow around blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart.
During CABG surgery, a skilled cardiac surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel, usually from another part of the body such as the leg or chest wall, and attaches it to bypass the damaged section of the artery. This creates an alternate route for blood to reach the heart muscle, improving its supply and reducing symptoms.
The decision to undergo CABG surgery is typically made after careful consideration by both patient and medical professionals. Factors such as severity of symptoms, extent of blockages in the arteries, overall health condition, and response to other treatment options are taken into account.
The procedure itself is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. The surgeon makes an incision in the chest and uses special instruments to access the heart. The bypass grafts are carefully connected to reroute blood flow around blocked areas. Once completed, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples.
Recovery from CABG surgery varies from person to person but generally involves a hospital stay of about one week. During this time, patients are closely monitored by healthcare professionals who ensure proper healing and manage pain effectively. Post-surgery rehabilitation programs may be recommended to help restore strength and improve cardiovascular fitness.
CABG surgery has proven to be highly successful in improving the quality of life for many individuals with coronary heart disease. It can alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of future heart attacks, and increase life expectancy. However, it is important to note that CABG surgery is not a cure for heart disease. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking are crucial in maintaining long-term heart health.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with CABG surgery. These can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, stroke, or damage to surrounding organs. However, advancements in surgical techniques and post-operative care have significantly reduced the occurrence of these complications.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of coronary heart disease or have been diagnosed with blocked arteries, it is essential to consult with a qualified cardiac specialist. They will assess your individual situation and determine whether CABG surgery is the most appropriate course of action.
CABG surgery has transformed the lives of countless individuals by restoring blood flow to the heart and improving overall cardiac function. With ongoing advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, this procedure continues to offer hope and improved outcomes for those affected by coronary heart disease.
What are the risks of CABG surgery?
While Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery is generally safe and effective, like any surgical procedure, it carries certain risks. It’s important to be aware of these potential complications and discuss them with your healthcare provider before making a decision. Some of the risks associated with CABG surgery include:
- Infection: There is a small risk of developing an infection at the site of the surgical incision or in the chest cavity. Precautions are taken to minimize this risk, including sterile operating environments and antibiotic prophylaxis.
- Bleeding: During and after surgery, there is a possibility of bleeding from the incision site or at the connection points of the bypass grafts. Surgeons take precautions to control bleeding during the procedure, but occasionally additional interventions may be required.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in response to surgery, particularly in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism). Medications such as blood thinners are often prescribed post-surgery to reduce this risk.
- Stroke: Although rare, there is a small risk of stroke during or after CABG surgery. This can occur due to clots forming in blood vessels supplying the brain or from other factors related to the procedure.
- Heart Attack: While CABG surgery aims to improve blood flow to the heart, there is still a small risk of heart attack during or after the procedure due to complications such as blood clots or disruptions in blood flow.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can occur following CABG surgery. Most arrhythmias are temporary and resolve on their own, but some may require medication or other interventions for management.
- Lung Problems: The use of a heart-lung machine during CABG surgery can temporarily affect lung function, leading to conditions like pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Breathing exercises and early mobilization are often employed to mitigate these risks.
- Kidney Problems: In some cases, CABG surgery can lead to temporary or permanent kidney dysfunction due to changes in blood flow and the use of medications during the procedure.
- Wound Healing Issues: Some individuals may experience delayed wound healing or infection at the incision site, especially if they have certain risk factors such as diabetes or obesity.
It’s important to note that while these risks exist, they are generally low, and complications can often be managed effectively with prompt medical attention. Your healthcare team will closely monitor you during and after surgery to minimize these risks and provide appropriate care.
It’s crucial to have open and honest discussions with your surgeon about the potential risks specific to your situation. They will be able to provide you with personalized information based on your medical history, overall health, and individual risk factors.
How long does CABG surgery take?
The duration of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery can vary depending on various factors, including the complexity of the case and the number of bypass grafts required. On average, CABG surgery typically takes around 3 to 6 hours to complete.
During this time, the surgical team will carefully perform the necessary steps to create new pathways for blood flow around blocked or narrowed arteries. This involves harvesting healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body, such as the leg or chest wall, and attaching them to bypass the damaged sections of the coronary arteries.
It’s important to note that while the surgery itself may take several hours, additional time is required for pre-operative preparations and post-operative monitoring. Before surgery, patients undergo anesthesia induction and are prepared for the procedure. Afterward, they are closely monitored in a recovery area as they awaken from anesthesia.
Recovery times can vary as well, with patients typically staying in the hospital for about one week following CABG surgery. This allows healthcare professionals to ensure proper healing and manage any potential complications effectively.
It’s worth mentioning that these timeframes are general estimates and can differ depending on individual circumstances. The surgeon will provide more specific information regarding expected duration based on your unique case during pre-operative consultations.
What is the recovery time for CABG surgery?
The recovery time for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery can vary from person to person, depending on several factors, including the individual’s overall health, age, and the extent of the procedure. However, a general timeline for recovery can be outlined.
In the immediate postoperative period, patients are typically monitored in the intensive care unit (ICU) for a day or two. During this time, medical professionals closely monitor vital signs and ensure proper healing. Pain management is also a priority to keep patients comfortable.
After leaving the ICU, patients are usually transferred to a regular hospital room where they continue their recovery. The hospital stay after CABG surgery typically ranges from five to seven days. During this time, healthcare professionals provide necessary medications, monitor progress, and help patients regain strength through light physical activity.
Once discharged from the hospital, patients are advised to continue their recovery at home. It is important to follow all postoperative instructions provided by the healthcare team. This may include taking prescribed medications, maintaining proper wound care, and gradually increasing physical activity as directed.
The initial recovery period at home usually lasts around six to eight weeks. During this time, individuals should take it easy and avoid strenuous activities that could strain the chest incision site or put stress on the healing heart.
Cardiac rehabilitation programs are often recommended as part of the recovery process. These programs typically start a few weeks after surgery and involve supervised exercise sessions tailored to each patient’s needs. They also provide education on heart-healthy lifestyle choices and support for emotional well-being.
It is important to note that while most individuals experience significant improvement within a few months after CABG surgery, full recovery can take several months or even up to a year. The pace of recovery varies among individuals; some may recover more quickly while others may require more time.
Throughout the recovery period, regular follow-up appointments with the cardiac surgeon or cardiologist are essential to monitor progress, address any concerns, and make necessary adjustments to medications or lifestyle recommendations.
It’s important to remember that each person’s recovery journey is unique, and it is crucial to listen to your body and follow the guidance of your healthcare team. By adhering to the prescribed recovery plan, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking ongoing medical care, individuals can optimize their chances of a successful recovery after CABG surgery.
How successful is CABG surgery?
CABG surgery, or coronary artery bypass grafting, is considered a highly successful procedure for treating coronary heart disease. The success rate of CABG surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the patient’s overall health condition, the severity and location of blockages in the arteries, and the expertise of the surgical team.
In general, CABG surgery has been shown to provide significant relief from symptoms and improve long-term outcomes for patients. Studies have indicated that CABG surgery can effectively alleviate chest pain (angina), improve exercise capacity, and enhance overall quality of life.
Moreover, CABG surgery has demonstrated positive results in reducing the risk of future heart attacks and prolonging life expectancy. By bypassing blocked or narrowed arteries, blood flow to the heart muscle is restored, reducing strain on the heart and lowering the likelihood of further cardiovascular complications.
The success rate of CABG surgery is also influenced by post-operative care and lifestyle modifications. It is crucial for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding medication use, dietary changes, regular exercise, smoking cessation (if applicable), and ongoing monitoring of cardiovascular health.
It is important to note that like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with CABG surgery. These can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, stroke, or damage to surrounding organs. However, advancements in surgical techniques and post-operative care have significantly reduced the occurrence of these complications.
Overall, when performed by experienced surgeons in appropriate cases with careful patient selection and comprehensive post-operative care, CABG surgery has a high success rate in improving symptoms, reducing future cardiac events, and enhancing quality of life for individuals with coronary heart disease.
Are there any alternatives to CABG surgery?
While CABG surgery is a highly effective treatment for coronary heart disease, there are alternative options that may be considered depending on individual circumstances. It’s important to note that the suitability of these alternatives varies based on factors such as the severity and location of blockages, overall health condition, and the presence of other medical conditions. Consulting with a cardiac specialist is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
- Medications: In some cases, medications can be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve blood flow. Medications such as aspirin, beta-blockers, statins, and nitroglycerin may be used to reduce chest pain (angina), lower cholesterol levels, control blood pressure, prevent blood clots, and improve overall heart function.
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Also known as coronary angioplasty or stenting, PCI is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a catheter with a small balloon into the blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to widen the artery and improve blood flow. In some cases, a stent (a small mesh tube) may be placed to keep the artery open.
- Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP): This non-invasive therapy involves using cuffs wrapped around the legs to compress and release them in sync with the heartbeat. This process improves blood flow to the heart by increasing collateral circulation.
- Transmyocardial Revascularization (TMR): TMR is a surgical procedure that uses laser technology to create channels in areas of the heart muscle without adequate blood supply. These channels stimulate new blood vessel growth and improve blood flow.
- Robotic-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery: With advancements in surgical techniques, some patients may be candidates for minimally invasive procedures performed using robotic assistance. These procedures involve smaller incisions and robotic arms controlled by surgeons for precise movements during surgery.
It’s important to remember that these alternatives may not be suitable for everyone, and the decision regarding the most appropriate treatment option should be made in consultation with a cardiac specialist. They will consider individual factors and recommend the best course of action to ensure optimal outcomes for each patient.
Is there any follow-up care after CABG surgery?
Yes, follow-up care is an important aspect of the recovery process after CABG surgery. It involves regular check-ups and monitoring to ensure proper healing, manage any potential complications, and support the patient’s overall well-being. The specific follow-up care plan may vary depending on individual circumstances, but here are some common aspects:
- Hospital Stay: After the surgery, patients typically remain in the hospital for about a week or until they are stable and ready to continue recovery at home.
- Medications: Patients are usually prescribed medications to manage pain, prevent infection, control blood pressure, and reduce the risk of blood clots. It is important to take these medications as prescribed and discuss any concerns or side effects with the healthcare team.
- Wound Care: Proper care of the surgical incision site is crucial for healing and preventing infection. Patients will receive instructions on how to clean and dress the wound, as well as when to seek medical attention if any signs of infection or complications arise.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is essential for long-term success after CABG surgery. This may include following a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, engaging in regular exercise as recommended by healthcare professionals, quitting smoking if applicable, managing stress levels, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Many patients are referred to cardiac rehabilitation programs that provide supervised exercise sessions, education on heart-healthy living, dietary guidance, and emotional support. These programs help individuals regain strength, improve cardiovascular fitness, and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
- Follow-up Appointments: Patients will have scheduled follow-up appointments with their cardiac surgeon or cardiologist to monitor progress and address any concerns or questions that may arise during recovery. These appointments may include physical examinations, blood tests, imaging tests (such as echocardiograms), or other diagnostic procedures as needed.
- Emotional Support: Recovering from CABG surgery can be emotionally challenging. Patients may experience a range of emotions, including anxiety, depression, or fear of future heart problems. It is important to seek support from loved ones, join support groups, or consider counseling services to help cope with these emotions.
It is crucial to adhere to the recommended follow-up care plan and attend all scheduled appointments. This helps ensure the best possible outcomes and allows healthcare professionals to monitor progress, address any issues promptly, and provide ongoing guidance for optimal recovery and long-term heart health.